Why Your Car’s Transmission Might Be Acting Up: Understanding Torque Converter Symptoms
The torque converter is a crucial component in a car’s transmission system. It plays a vital role in transferring power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move smoothly and efficiently. Understanding how the torque converter works and recognizing the signs of a faulty one can help prevent further damage and costly repairs.
What is a torque converter?
A torque converter is a fluid coupling device that connects the engine to the transmission in an automatic car. It allows the engine to continue running even when the vehicle is at a complete stop, without stalling. In essence, it serves as a mediator between the engine and the transmission, ensuring that power is transferred smoothly.
In comparison to a clutch in a manual transmission, which requires the driver to engage and disengage it manually, a torque converter operates automatically. This makes it easier for drivers to operate their vehicles, as they do not need to worry about shifting gears or engaging and disengaging the clutch.
How does a torque converter work?

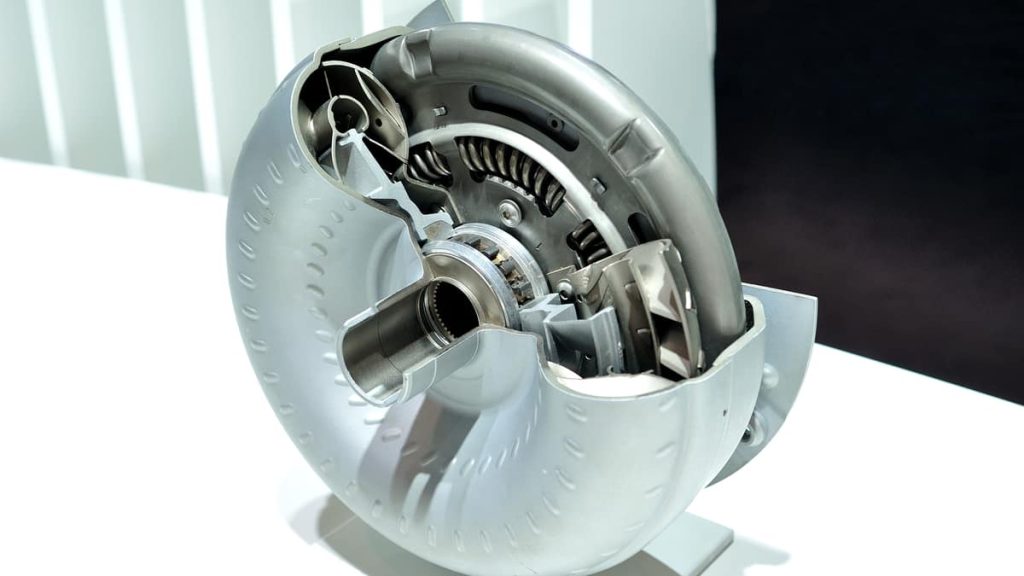
A torque converter consists of three main components: the impeller, turbine, and stator. The impeller is connected to the engine’s crankshaft and is responsible for driving the fluid inside the torque converter. The turbine is connected to the transmission input shaft and receives power from the impeller. The stator sits between the impeller and turbine and helps redirect fluid flow for increased efficiency.
The process begins when the engine starts running, causing the impeller to spin and create fluid flow inside the torque converter. This fluid flow then drives the turbine, which transfers power to the transmission input shaft. The stator helps redirect fluid flow by changing its direction before it returns to the impeller.
Why is the torque converter important for your car’s transmission?
The torque converter plays a crucial role in a car’s transmission system. It allows for smooth power transfer from the engine to the wheels, ensuring that the vehicle can accelerate and maintain speed without any issues. Without a properly functioning torque converter, the transmission system would not be able to operate effectively, leading to poor vehicle performance and potential damage to other components.
Proper functioning of the torque converter is essential for overall vehicle performance. It allows the engine to operate at its optimal RPM range, ensuring efficient power delivery. A faulty torque converter can result in a loss of power, decreased fuel efficiency, and even transmission overheating. Therefore, it is important to address any symptoms of torque converter issues promptly.
Common symptoms of a faulty torque converter
There are several common signs that indicate a faulty torque converter. These symptoms may vary depending on the severity of the issue, but it is important to recognize them early on to prevent further damage. Some common symptoms include:
- Slipping or shuddering: A slipping or shuddering sensation when accelerating or shifting gears can indicate a problem with the torque converter. This may be caused by worn-out clutch plates or a damaged stator.
- Delayed engagement: If there is a delay in the vehicle’s response when shifting from park to drive or reverse, it could be a sign of a faulty torque converter. This delay may be accompanied by a high-pitched whining noise.
- Overheating: A malfunctioning torque converter can cause the transmission fluid to overheat. This can lead to transmission failure if not addressed promptly. Signs of overheating include a burning smell, fluid leaks, or the transmission slipping out of gear.
- Increased fuel consumption: A faulty torque converter can result in decreased fuel efficiency. If you notice that your vehicle is consuming more fuel than usual, it may be due to an issue with the torque converter.
- Check engine light: In some cases, a faulty torque converter can trigger the check engine light on your dashboard. This is often accompanied by error codes related to the transmission system.
How to diagnose torque converter problems
Diagnosing torque converter problems requires a systematic approach and the use of specialized tools. Here is an overview of the diagnostic process:
- Visual inspection: Start by visually inspecting the torque converter for any signs of damage or leaks. Look for fluid leaks, cracks, or excessive wear on the components.
- Fluid level and condition: Check the transmission fluid level and condition. Low fluid levels or dirty fluid can indicate a problem with the torque converter.
- Scan for error codes: Use a diagnostic scanner to retrieve any error codes related to the transmission system. These codes can provide valuable information about the specific issue with the torque converter.
- Test drive: Take the vehicle for a test drive and pay attention to any abnormal noises, vibrations, or slipping sensations. Note any changes in performance during acceleration or shifting gears.
- Pressure testing: Use a pressure gauge to measure the hydraulic pressure inside the torque converter. Low pressure can indicate a problem with the impeller, turbine, or stator.
What causes torque converter issues?
There are several common causes of torque converter problems. Understanding these causes can help prevent issues and prolong the lifespan of your torque converter. Some common causes include:
- Fluid contamination: Contaminated transmission fluid can cause damage to the torque converter’s components, leading to issues such as slipping or overheating. Contamination can occur due to dirty fluid or the presence of debris in the transmission system.
- Worn-out clutch plates: Over time, the clutch plates inside the torque converter can wear out, resulting in slipping or shuddering during acceleration or shifting gears.
- Damaged stator: The stator plays a crucial role in redirecting fluid flow for increased efficiency. If it becomes damaged or worn out, it can cause issues such as slipping or delayed engagement.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can cause the torque converter to malfunction. This can be caused by low fluid levels, dirty fluid, or towing heavy loads for extended periods.
Can a torque converter be repaired or does it need to be replaced?
Whether a torque converter can be repaired or needs to be replaced depends on the extent of the damage and the specific issue. In some cases, minor issues such as fluid leaks or worn-out clutch plates can be repaired without replacing the entire torque converter. However, if the damage is severe or if multiple components are affected, it may be more cost-effective to replace the torque converter altogether.
Factors that determine whether a torque converter can be repaired or needs to be replaced include the availability of replacement parts, the cost of repairs versus replacement, and the expertise of the technician performing the repairs.
How much does it cost to fix a torque converter?

The cost of fixing a torque converter can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of your vehicle, the extent of the damage, and whether you choose to repair or replace the torque converter. On average, the cost of repairing a torque converter can range from $500 to $1500, while replacing it can cost anywhere from $1000 to $2500.
Additional costs may include labor charges, fluid replacement, and any other necessary repairs or replacements in the transmission system. It is important to consult with a qualified technician to get an accurate estimate for your specific vehicle.
How to prevent torque converter problems in the future
Regular maintenance and proper care can help prevent torque converter problems in the future. Here are some tips for maintaining your torque converter and transmission system:
- Regular fluid checks: Check the transmission fluid regularly and ensure that it is at the correct level. If the fluid appears dirty or has a burnt smell, it may need to be replaced.
- Fluid flushes: Consider getting a transmission fluid flush every 30,000 to 60,000 miles. This helps remove any contaminants and ensures that the fluid is clean and in good condition.
- Avoid excessive heat: Avoid towing heavy loads for extended periods or driving in extreme conditions that can cause the transmission fluid to overheat. This can help prevent damage to the torque converter.
- Regular inspections: Have your torque converter and transmission system inspected regularly by a qualified technician. They can identify any potential issues early on and address them before they become major problems.
- Follow manufacturer’s recommendations: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your vehicle. This includes regular service intervals and fluid changes.
Conclusion: The importance of addressing torque converter symptoms promptly.
The torque converter is a crucial component in a car’s transmission system, allowing for smooth power transfer from the engine to the wheels. Recognizing the signs of a faulty torque converter and addressing them promptly is essential to prevent further damage and costly repairs.
By understanding how the torque converter works, diagnosing potential issues, and taking preventive measures, you can ensure that your vehicle’s transmission system operates smoothly and efficiently. Regular maintenance and proper care can help prolong the lifespan of your torque converter and prevent future problems.